What If You Dont Have Full 401 Vesting
The short answer is you dont have full ownership of your 401 plan balance. No matter how much money your 401 plan may have, you only actually own the amount that represents your own contributions to the plan, as well as any amount of employer matching contributions that have been vested.
But there are two important points to remember about 401 vesting. The first is its found money. Its always worth getting, but if you dont get it because you terminated your employment you really havent lost anything either. But its usually worth staying with an employer to get full 401 vesting, especially if youre just a year or two away from it.
The second point relates to the employer. Employers offer 401 plan contribution matches as an additional benefit to their employees. They are well aware of the fact that a good employer match provides a strong hiring incentive.
But since they are also anxious to minimize employee turnover, they use 401 vesting schedules to make sure their people stay around for a few years.
It works in both cases. As an employee, the employer match is a definite wealth enhancer. And from an employer standpoint, its a major reason why you are likely to stay with your employer for at least a few years.
And once youre fully vested, its all yours. Thats one of the best retirement deals there is.
How Do 401 Vesting Schedules Work
If you belong to a 401 plan youve probably heard the term vested mentioned somewhere along the line. But what exactly does it mean to be vested and how does a 401 vesting schedule affect the amount you have saved?
As it turns out, vesting can either have no effect at all or it can be extremely important. And I know that sounds crazy, but stick with me because today were going to teach you everything you need to know about 401 vesting rules
Lets dive in!
Types Of Money That Might Vest
Examples of money types that are most likely to have a vesting schedule include:
- Employer matching: Any funds you receive as a result of your own contributions to the plan.
- Employer profit-sharing: Money you might get regardless of whether or not you contribute.
- Others, potentially
Examples of contributions that would generally not require any wait for vesting:
- Qualified non-elective contribution : An employer contribution thats typically used to fix mistakes or solve failed discrimination tests. For the contribution to work, it must be 100% immediately vested.
- Qualified matching contribution : Similar to a QNEC, above, but handled differently.
- Rollover: Funds that you roll into your plan from a previous employers 401, 403, your IRA, etc.
IRA-based accounts, including SEPs and SIMPLEs, do not have vesting schedules. Once the money goes into your account, its yours to do with as you please. However, its critical to learn about potential tax consequences of moving or withdrawing funds from any retirement account.
Important: Speak with your tax advisor and your plan administrator before making any decisions. The information here might not apply to your plan, it may be outdated, or there may be errors or omissions that you need to address with a professional.
Next Up: Curious About Meeting?
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get 401k
What Vesting Schedules Can I Select For My Plan
The Internal Revenue Code provides two acceptable vesting schedules 401 and profit sharing plans: three-year cliff and two- to six-year graded. Under a three-year cliff vesting schedule, participants are 100% vested in the employer contributions when they are credited with three years of vesting service, but are 0% vested at all prior points. Under two- to six-year graded vesting, participants are increasingly vested in the employer contributions with each passing year. The below chart shows the vesting percentages for both possible schedules.
|
Three-Year Cliff |
|
100% |
Employers can adopt vesting schedules more favorable to their employees. For example, an employer could have participants fully vest after two years or have participants increase their vested percentage by 25% per year for four years . Both of these schedules are allowed because participants vest faster under these schedules than they do under the IRCs schedules above.
There is a special safe harbor 401 plan that provides for automatic enrollment, called a Qualified Automatic Contribution Arrangement . Employer contributions under a QACA may have a two-year vesting schedule.
Should I Take Advantage Of My Employer Match Even If I’m Planning To Leave
It never hurts to sign up and take advantage of the employer match, even if you’re not planning on staying at your job long enough to become fully vested in your 401. You may end up staying at your job longer than you originally planned, and you may end up being able to keep some of that money for your retirement.
And remember: When it comes to retirement, it’s always better to save more rather than less. Your future self will thank you.
Read Also: Where To Roll Over My 401k
What Does It Mean To Be Vested In My 401
The Balance
You know that you should contribute to your 401 on a regular basis and that you should match your employer’s contribution. You might even know that you should invest more aggressively when you’re young, then adjust to a more conservative approach as you near retirement age. But do you know what it means to be “vested” in your 401?
Vesting Schedules In A Nutshell
Investing in an employer-sponsored retirement plan can be a great way to save for the future. While employee contributions are always 100% vested, itâs important to understand that employer contributions may be vested over time. Reviewing your employerâs vesting schedule can help you plan the number of years of service youâll need before your matched contributions are vested.
Understanding your employerâs vesting schedule could help you to better plan for retirement. You may even find ways to become financially independent and retire earlyâa lifestyle also known as the FIRE movement.
We hope you found this helpful. Our content is not intended to provide legal, investment or financial advice or to indicate that a particular Capital One product or service is available or right for you. For specific advice about your unique circumstances, consider talking with a qualified professional.
Related Content
Also Check: How To Transfer My 401k To My New Job
If You See A Vested Balance On Your 401 Statement Here’s What That Number Is Telling You
401 matching contributions can be a wonderful perk for employees. Under an employer matching program, your employer agrees to contribute money to your 401 account, matching what you save from your own paycheck, pre-tax, up to a certain limit. For example, an employer might agree to match 100% of employees’401 contributions up to a maximum 5% of salary.
Matching is a terrific benefit, and more than 90% of employers that offer 401 plans provide a company match. However, the money your employer contributes typically isn’t yours right away, and you could lose it if you leave your job. In most cases, there is a point at which the funds your employer contributes legally become yours, and that’s where vesting comes in.
Here’s an example of how powerful an employer match can be: If your salary is $60,000 and you contribute 5%, you save $3,000 per year for retirement. But if your company offers a 50% match, it kicks in a total of $1,500 on top of your contribution, so your account actually receives an annual contribution of $4,500 — a nice sum that will compound over time to benefit you in retirement.
Whats A Good Employer Match And Vesting Percentage
A common annual employer match is 100% of the employee contribution up to 3% of one’s salary. This means that if you contribute $50 in each paycheck, the employer will match that $50 up to 3% of the paycheck amount. That means that if an employee makes $2,000 per paycheck, the employer will match up to $60 per paycheck. Contributing only $50 doesnât max out the free money an employee can get from the employer.
Read Also: How To Find Out If You Have A 401k
Basics Of A Vesting Schedule
To encourage employee loyalty, employers frequently make contributions to your retirement or stock-option account subject to a vesting plan. This incentive program set up by a company determines when you’ll be fully “vested” in, or acquire full ownership of, employer contributions to the plan.
Through a vesting schedule, employers dangle their contributions in front of you like a carrot. The more years you work for the firm, the more of the contributions you get to keep. If you leave before you are fully vested under the plan, some or all of the funds return to the company.
Vesting doesn’t apply to any money you contribute yourself. Whenever you make a contribution to your retirement plan at work, you are 100% vested in your own contributions. Vesting schedules apply only to funds that employers contribute on your behalf.
Why Would I Want A Vesting Schedule In My Plan
A vesting schedule helps incentivize employees to stay with the company. In addition, vesting schedules help reduce the cost of employer contributions over time, as employees who leave before their contributions are fully vested forfeit their right to the contributions, which can then be used to pay for plan expenses or fund contributions to other employees.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Money From Your 401k
What Events Will Cause Participants To Become 100% Vested
There are 3 major events that will cause participants to become 100% vested:
Plan sponsors often choose to fully vest participants in cases of death or disability, but they are not required to do so.
How Does 401 Vesting Actually Work

To start, lets take a look at how the IRS defines vesting:
Vesting in a retirement plan means ownership. This means that each employee will vest, or own, a certain percentage of their account in the plan each year. An employee who is 100% vested in his or her account balance owns 100% of it and the employer cannot forfeit, or take it back, for any reason. Amounts that are not vested may be forfeited by employees when they are paid their account balance.
In other words, its a schedule of terms setup by your employer that dictates when you technically own the 401 contributions that they have given you.
Notice that were only talking about the employer matching contributions. Your contributions, the money that you have personally invested into your 401 is always yours and yours to keep. In other words, you are always 100% vested in your own contributions.
Yes, the employer contributions that are often matched with 401 plans might not actually belong to you right away. Usually there is some amount of time you have to wait until they are yours.
Lets break this down with a real-life example.
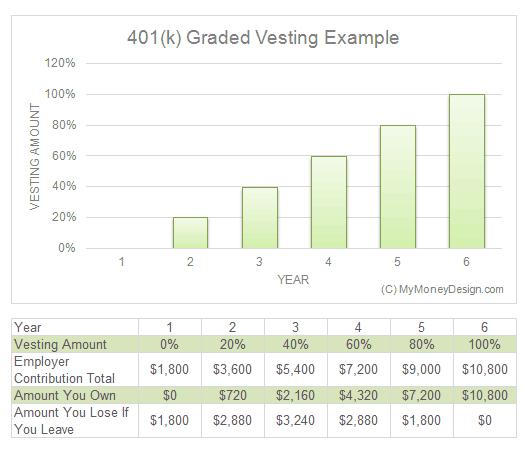
Graded Vesting Example:
My former employer had whats called a graded vestment plan. This is where you start off the 401 plan being 0% for the first year.
At the beginning of the second year, your vesting level rises to 20%. Then in the third year, it rises again to 40%. It continues this process until your sixth year when you finally become 100% vested.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Difference Between An Ira And A 401k
Are There Other Types Of Vesting
The graded vestment example I just gave is one common example. In reality, its up to the company to decide how employees get vested into their 401 plans.
A few other common ones include:
- Immediate. Just like it sounds. From the day you are hired, you are already 100% vested. All the 401 contributions are yours! This is the way my current employer handles vesting, and its great!
- Cliff. Cliff plans are when you are 0% vested for the first 1-2 years, and then immediately cross over into 100% vestment afterwards. Its sort of an all or nothing schedule.
Year of Service
Typically with all vesting plans, your progress is measured in years of service with the company. In general this is usually defined as 1,000 hours of work for the year.
Timing Of Permissible Distributions
In general, 401 plans may not make plan distributions to participants until a distributable event occurs. The distributable events must be defined in the plan document and, specifically, are based on the type of contributions involved. For 401 elective deferrals , distributable events are quite restrictive and are limited to the following events:
- A participants termination from employment
- A participants death
NOTE: Coronavirus-related distributions under the CARES Act Ease-of-Access and Other Provisions for details) have now expired.
For other plan contribution types, like employer matching contributions or discretionary employer contributions, the plan can be written to allow for less restrictive requirements for distribution. However, most 401 plans are written so that the same distribution requirements apply to all contribution types so that plan administration is simpler.
You May Like: Can I Transfer Money From 401k To Ira
Consequences Of A Late Distribution
- If the excess deferrals arent distributed from the plan by April 15, each affected plan of the employer is subject to disqualification and would need to go through the IRS Employee Plans Compliance Resolution System to correct the operational error.
- Under EPCRS, these excess deferrals are subject to double taxation that is, theyre taxed both in the year contributed to the plan and in the year distributed from the plan.
- These late distributions could also be subject to the 10% early distribution tax, 20% withholding and spousal consent requirements.
Qualifying Distributions From Designated Roth Accounts
If a plan includes Roth contributions, there are additional special distribution timing rules for the designated Roth account which must be followed in order for the special tax advantages to apply. In general, a 5-year period must be measured from the first day of the first year during which designated Roth contributions are made. If a participant takes a distribution from a designated Roth account before the end of the 5-year period that applies for the participant, the earnings on the Roth contributions become taxable and must be included in gross income at the time of distribution. If a participant takes a distribution from a designated Roth account after the end of the 5-year period that applies for the participant, the earnings on the Roth contributions remain tax-free on distribution. For more information regarding designated Roth contributions, .
Also Check: How Do I Get My 401k Early
Vesting Schedules For Private
If you have a pension plan, aka defined benefit plan, the laws for vesting are a little different. With a defined benefit plan, the longest a cliff vesting schedule can be is five years. If the company follows a graded schedule, it can require up to seven years of service in order to be 100% vested. But it must provide at least 20% vesting after three years, 40% after four years, 60% after five years and 80% after six years. If the defined benefit plan is a cash balance plan, employees must become fully vested after years or less.
When Can I Withdraw From A 401k
Having a fully vested 401k does not necessarily mean you are completely free to withdraw funds. With traditional 401k plans, you have to be at least 59½ years old before you can make withdrawals without incurring a tax. Withdrawing early can result in a 10% penalty in addition to any taxes from ordinary income.
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Roth 401k And Roth Ira
A Note On Uncovering Hidden Fees In Your 401 Investments
Most of us greatly under-estimate the impact that fees can have on our retirement. Thanks to the power of compound interest, even a seemingly harmless 0.5% difference in fees can cost you hundreds of thousands of dollars and delay your retirement by many years.
When InvestmentZen contributor Mr. 1500ran Personal Capitals fee analysis tool on his 401k portfolio, he was shocked by what he discovered. The free analysis showed that with his current portfolio, he was on track to paying a whopping $594,993 in fees over the next 26 years and losing 3 years of retirement, due entirely to hidden fees:
After making this discovery, it only took him a few hours of adjusting his portfolio with the help of Personal Capitals fee analyzer to reduce his potential fees to just $86,163, saving him over $500,000 dollars and shaving 2 years from his path to retirement.
If you want to get the most out of your 401 investments, signing up for a free account at Personal Capital to take advantage of their free investment fee analyzer is an easy way to do it.
It could potentially save you $500,000 dollars .
What Does 401k Vesting Mean

When your employer makes matching contributions to your 401k, they will often delay the transfer of ownership to you. Any funds you contribute yourself belong to you right away, but the company match amounts are typically transferred to you gradually over one or more years. This transfer of ownership is what is meant by the term vesting.
Once an employer match has fully vested, you have total ownership of those funds. You own them outright and they are yours to keep if you decide to leave your employer, are laid off, or even get fired.
You May Like: How To Invest 401k Rollover